Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Maritime, Port and Aviation Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-070, 70 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and development of the sample-return technique for fuel debris using the unmanned underwater vehicle" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop a fuel debris sampling device that comprises a neutron detector with radiation resistance and enhanced neutron detection efficiency, an end-effector with powerful cutting and collection capabilities, and a manipulator under the Japan-UK joint research team. We will also develop a fuel debris sampling system that can be mounted on an unmanned vehicle. In addition, we will develop a positioning system to identify the system position, and a technique to project the counting information of optical cameras, sonar, and neutron detectors to be developed ...
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Civil)Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Maritime, Port and Aviation Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-049, 67 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and development of the sample-return technique for fuel debris using the unmanned underwater vehicle" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to develop a fuel debris sampling device that comprises a neutron detector with radiation resistance and enhanced neutron detection efficiency, an end-effector with powerful cutting and collection capabilities, and a manipulator under the Japan-UK joint research team. We will also develop a fuel debris sampling system that can be mounted on an unmanned vehicle. In addition, we will develop a positioning system to identify the system position, and a technique to project the counting information of optical cameras, sonar, …
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru
JAEA-Review 2020-068, 114 Pages, 2021/03
Radiation safety regulations have been currently established based on the 1990Recommendation by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in Japan. Meanwhile, ICRP released the 2007 Recommendation that replaces the 1990 Recommendation. Thus, the Radiation Council, which is established under the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), has made discussions to incorporate the purpose of the 2007 Recommendation into Japanese regulations for radiation safety. As ICRP also has published effective dose coefficients for internal exposure assessment in accordance with the 2007recommendation, the technical standards are to be revised for the internal exposure assessment method in Japan. Currently, not all of the effective doses have been published to revise concentration limits for internal exposure protections of workers and public. The published effective dose coefficients are applied to radionuclides which are important in radiation protection for internal exposure of a worker. Thus, we review new effective dose coefficients as well as basic dosimetry models and data based upon Occupational Intakes of Radionuclides (OIR) parts 2, 3 and 4 that have been published from 2016 to 2019 by ICRP. In addition, issues are sorted out to provide information for revision of the technical standards for internal exposure assessment based on the 2007 Recommendations in future.
 for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo technique
for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo techniqueIwamoto, Hiroki; Stankovskiy, A.*; Fiorito, L.*; Van den Eynde, G.*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 4, p.42_1 - 42_7, 2018/11
This paper presents a nuclear data sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the effective delayed neutron fraction  for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The
for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The  sensitivities are calculated by the modified
sensitivities are calculated by the modified  -ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the
-ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the  sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors
sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors  introduced by Chiba shows that a value of
introduced by Chiba shows that a value of 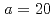 is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of
is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of  . Using the calculated
. Using the calculated  sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the
sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the  uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2
uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2  0.2% and 2.0
0.2% and 2.0  0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of
0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of  Pu and
Pu and  U.
U.
Yamamoto, Kento*; Akie, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya; Hosoyamada, Ryuji*
JAEA-Technology 2015-019, 110 Pages, 2015/10
In the direct disposal of used nuclear fuel (UNF), criticality safety evaluation is one of the important issues since UNF contains some amount of fissile material. The recent development of higher-enrichment fuel has enhanced the benefit of the application of Burnup Credit. In the present study, the effects of the several parameters on the reactivity of disposal canister model were evaluated for used PWR fuel. The parameters are relevant to the uncertainties of depletion calculation code, irradiation history, and axial and horizontal burnup distribution, which are known to be important effect in the criticality safety evaluation adopting burnup credit. The latest data or methodology was adopted in this evaluation, based on the various latest studies. The appropriate margin of neutron multiplication factor in the criticality safety evaluation for UNF can be determined by adopting the methodology described in the present study.
Okumura, Keisuke
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-015, 162 Pages, 2015/10
MOSRA-SRAC is a lattice calculation module of the Modular code System for nuclear Reactor Analyses (MOSRA). This module performs the neutron transport calculation for various types of fuel elements including existing light water reactors, research reactors, etc. based on the collision probability method with a set of the 200-group cross-sections generated from the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-4.0. It has also a function of the isotope generation and depletion calculation for up to 234 nuclides in each fuel material in the lattice. In these ways, MOSRA-SRAC prepares the burn-up dependent effective microscopic and macroscopic cross-section data to be used in core calculations.
 U doppler effect in the soft neutron spectra using FCA (Joint research)
U doppler effect in the soft neutron spectra using FCA (Joint research)Ando, Masaki; Kawasaki, Kenji*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Matsuura, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Yuji*
JAERI-Research 2005-026, 39 Pages, 2005/09
 U Doppler effect measurements in moderated neutron spectra (uranium fuel and MOX simulated fuel) were carried out using FCA for the purpose of contributing to the improvement in prediction accuracy for Doppler coefficient in LWR. In the mockup cores for MOX fuel, the measurements were performed in different neutron spectra, where the voidage of moderator material was varied systematically. The experimental data were obtained using cylindrical uranium samples with different outer diameter up to 800
U Doppler effect measurements in moderated neutron spectra (uranium fuel and MOX simulated fuel) were carried out using FCA for the purpose of contributing to the improvement in prediction accuracy for Doppler coefficient in LWR. In the mockup cores for MOX fuel, the measurements were performed in different neutron spectra, where the voidage of moderator material was varied systematically. The experimental data were obtained using cylindrical uranium samples with different outer diameter up to 800 C. Analyses were performed using a standard code system designed to analyze fast reactor mock-up experiments at FCA with the use of the JENDL-3.2 library. The results of the analyses showed that the calculation accuracy did not depend on the types of the core fuel or the Doppler samples. The calculated values agreed with the experimental ones within the experimental error. Any dependency of the prediction accuracy on the neutron spectra was not observed in the MOX simulated fuel cores.
C. Analyses were performed using a standard code system designed to analyze fast reactor mock-up experiments at FCA with the use of the JENDL-3.2 library. The results of the analyses showed that the calculation accuracy did not depend on the types of the core fuel or the Doppler samples. The calculated values agreed with the experimental ones within the experimental error. Any dependency of the prediction accuracy on the neutron spectra was not observed in the MOX simulated fuel cores.
Tran, V. H.; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Tsuda, Shuichi; Endo, Akira; Saito, Kimiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Tech 2004-079, 37 Pages, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Ando, Masaki; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okajima, Shigeaki; Kawasaki, Kenji
JAERI-Research 2003-029, 72 Pages, 2003/12
The objectives of this study is to clarify calculation accuracy for the Doppler effect of the resonance materials; erbium (Er), tungsten (W) and thorium (ThO ). Doppler effect measurements were carried out in a fast neutron spectrum (XX-2 core) and in an intermediate neutron spectrum (XXI-1D2 core) by the sample-heated and reactivity worth measurement method up to 800
). Doppler effect measurements were carried out in a fast neutron spectrum (XX-2 core) and in an intermediate neutron spectrum (XXI-1D2 core) by the sample-heated and reactivity worth measurement method up to 800 C using FCA. The experiment was analyzed with the standard analysis method for fast reactor cores at FCA with the use of the JENDL-3.2. The SRAC system was also used to investigate the calculation accuracy of the system and to compare it with that of the FCA standard analysis method. The standard analysis method underestimated for the XX-2 core and agreed the experiments within the experimental errors for the XXI-1D2 core. The analysis with the SRAC system gave smaller values by 3%
C using FCA. The experiment was analyzed with the standard analysis method for fast reactor cores at FCA with the use of the JENDL-3.2. The SRAC system was also used to investigate the calculation accuracy of the system and to compare it with that of the FCA standard analysis method. The standard analysis method underestimated for the XX-2 core and agreed the experiments within the experimental errors for the XXI-1D2 core. The analysis with the SRAC system gave smaller values by 3% 10% for the Er sample and bigger values by 2%
10% for the Er sample and bigger values by 2% 5% for the W sample than the standard analysis method.
5% for the W sample than the standard analysis method.
Kuroishi, Takeshi; Hoang, A.; Nomura, Yasushi; Okuno, Hiroshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-021, 60 Pages, 2003/03
The reactivity effect of the asymmetry of axial burnup profile is studied for PWR spent fuel transport cask proposed in OECD/NEA Phase II-C benchmark. The axial burnup profiles are based on in-core flux measurements. Criticality calculations are performed with the continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP-4B2 and the nuclear data library JENDL-3.2. Calculations are carried out not only for cases in the benchmark but also for symmetric burnup cases. Both actinide-only approach and actinide plus fission product approach is considered. The end effect is more sensitive to higher burnup asymmetry. The axial fission distribution becomes strongly asymmetric as its peak shifts toward the fuel top end. The peak of fission distribution gets higher with the increase of either the burnup asymmetry or the assembly-averaged burnup. The conservatism of uniform axial burnup assumption for the actinide-only approach is estimated quantitatively in comparison with the keff result calculated with experiment-based strongest asymmetric axial burnup profile for the actinide plus fission product approach.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Sakai, Tomohiro*
Nuclear Technology, 140(3), p.255 - 265, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to facilitate discussions based on quantitative analysis about the end effect, which is often talked about in connection to burnup credit in criticality safety evaluation of spent fuel, we introduced in this paper a burnup importance function. This function shows the burnup effect on the reactivity as a function of the fuel position; an explicit expression of this function was derived according to the perturbation theory. The burnup importance function was applied to the Phase IIA benchmark model that was adopted by the OECD/NEA Expert Group on Burnup Credit Criticality Safety. The function clearly displayed that burnup importance of the end regions increases (1) as burnup, (2) as cooling time, (3) in consideration of burnup profile, and (4) in consideration of fission products.
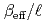 measurement on low enriched uranyl nitrate solution with single unit cores (600
measurement on low enriched uranyl nitrate solution with single unit cores (600 , 280T, 800
, 280T, 800 ) of STACY
) of STACYTonoike, Kotaro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(11), p.1227 - 1236, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kinetic parameter 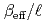 of low enriched uranyl nitrate solution was measured by the pulsed neutron source method in the STACY. This measurement was repeated systematically over several uranium concentrations from 193.7 gU/
of low enriched uranyl nitrate solution was measured by the pulsed neutron source method in the STACY. This measurement was repeated systematically over several uranium concentrations from 193.7 gU/ to 432.1 gU/
to 432.1 gU/ . Used core tanks were two cylindrical tanks whose diameters are 600 mm and 800 mm and one slab tank which has 280 mm thickness and 700 mm width. In this report, experimental data such as solution conditions, critical solution level for each solution condition, subcritical solution levels where measurements were conducted, measured decay time constants of prompt neutron and extrapolated
. Used core tanks were two cylindrical tanks whose diameters are 600 mm and 800 mm and one slab tank which has 280 mm thickness and 700 mm width. In this report, experimental data such as solution conditions, critical solution level for each solution condition, subcritical solution levels where measurements were conducted, measured decay time constants of prompt neutron and extrapolated 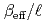 values are described as well as basic principle of the pulsed neutron source method.
values are described as well as basic principle of the pulsed neutron source method. 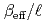 values were evaluated also by computation with the diffusion code CITATION in SRAC and the nuclear data library JENDL 3.2. Both experimental and computational
values were evaluated also by computation with the diffusion code CITATION in SRAC and the nuclear data library JENDL 3.2. Both experimental and computational 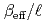 values show good agreement.
values show good agreement.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Sakai, Tomohiro*
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2002/10
As the burnup proceeds, reactivity of fuel assemblies for light water reactors decreases by depletion of fissile nuclides, especially in the axially central region. In order to describe the importance of the end regions to the reactivity change, a burnup importance function was introduced as a weighting function to a local burnup variation contributed to a reactivity decrease. The function was applied to the OECD/NEA/BUC Phase II-A model and a simplified Phase II-C model. The application to Phase II-A model clearly showed that burnup importance of the end regions increases as burnup and/or cooling time increases. Comparison of the burnup importance function for different initial enrichments was examined. The application result to the simplified Phase II-C model showed that the burnup importance function was helpful to find the most reactive fuel burnup distribution under the conditions that the average fuel burnup was kept constant and the variations in the fuel burnup were within the maximum and minimum measured values.
 U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu by using results of in-pile measurements of effective delayed neutron fraction
Pu by using results of in-pile measurements of effective delayed neutron fractionSakurai, Takeshi; Okajima, Shigeaki
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2002/10
The cross section adjustment method was applied to total delayed neutron yields of  U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu of the JENDL-3.2 file by using experimental results of effective delayed neutron fraction
Pu of the JENDL-3.2 file by using experimental results of effective delayed neutron fraction 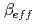 at six cores built in two fast critical facilities of the MASURCA and FCA and a thermal critical facility of the TCA to improve these yields. The adjustment was carried out on the yields given at several incident neutron energy points in the file. Furthermore, to validate these adjusted delayed neutron yields, analyses were performed for the
at six cores built in two fast critical facilities of the MASURCA and FCA and a thermal critical facility of the TCA to improve these yields. The adjustment was carried out on the yields given at several incident neutron energy points in the file. Furthermore, to validate these adjusted delayed neutron yields, analyses were performed for the 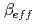 experiments at ZPR fast critical facility. These adjusted yields brought a reduction of uncertainty of calculated
experiments at ZPR fast critical facility. These adjusted yields brought a reduction of uncertainty of calculated 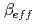 and an improvement in agreement of
and an improvement in agreement of 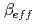 between experiment and calculation.
between experiment and calculation.
Takizuka, Tomonori; Hojo, Hitoshi*; Hatori, Tadatsugu*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(9), p.857 - 912, 2002/09
Transport along field lines in magnetic confinement plasmas is reviewed. Collisionless and collisional-diffusive transports are discussed. Because of their fast transport, features of plasmas along field lines are apt to behave nonlocally. A nonlocal phenomenon of scrape-off layer (SOL) and divertor plasmas in a tokamak is introduced, whose asymmetry along field lines is induced by the thermoelectric instability related to the SOL current. A local phenomenon called MARFE can be brought by the strong radiation cooling. The "snake" with nonlocal feature along field lines but with local structure perpendicular to the field is observed in a tokamak core plasma. For mirror-confined plasmas, axial particle losses from the mirror ends, especially pitch-angle-sattering losses into the loss cone and nondiabatic losses due to the breakdown of adiabaticity of the magnetic moment, are also discussed in the relation to nonlocal axial transport.
Igarashi, Shinichi; Muto, Shunsuke*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Kiichi
Surface & Coatings Technology, 158-159, p.421 - 425, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
 U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu in JENDL-3.2 using benchmark experiments on effective delayed neutron fraction
Pu in JENDL-3.2 using benchmark experiments on effective delayed neutron fraction 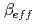
Sakurai, Takeshi; Okajima, Shigeaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(1), p.19 - 30, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)The cross section adjustment method was applied to total delayed neutron yields of  U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu of the JENDL-3.2 file by using experimental results of effective delayed neutron fraction
Pu of the JENDL-3.2 file by using experimental results of effective delayed neutron fraction 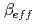 at six cores built in two fast critical facilities of the MASURCA and FCA and a thermal critical facility of the TCA to improve these yields. The adjustment was carried out on the yields given at several incident neutron energy points in the file. After the adjustment, the yield of
at six cores built in two fast critical facilities of the MASURCA and FCA and a thermal critical facility of the TCA to improve these yields. The adjustment was carried out on the yields given at several incident neutron energy points in the file. After the adjustment, the yield of  U was almost uniformly decreased by about 3% below 7 MeV. The yield of
U was almost uniformly decreased by about 3% below 7 MeV. The yield of  Pu was increased by 2.6% and that of
Pu was increased by 2.6% and that of  U was decreased by 0.9% at the thermal energy point, while the change of yield was less than 0.3% at the other energy points for these nuclides. By using these adjusted yields, the uncertainty of calculated
U was decreased by 0.9% at the thermal energy point, while the change of yield was less than 0.3% at the other energy points for these nuclides. By using these adjusted yields, the uncertainty of calculated 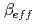 was reduced and the agreement of
was reduced and the agreement of 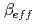 between experiment and calculation was improved.
between experiment and calculation was improved.
Nakajima, Ken
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(12), p.1120 - 1125, 2001/12
no abstracts in English